Classic Packing has the biggest stock-supported range of fabrics in China since we work together with over 80 trustworthy fabric manufacturers. We can satisfy all of your fabric needs of wholesale makeup bads and related packing products. If you cant find the fabric you need to custom your products. Please feel free to CONTACT US. We will fulfill your needs.
-
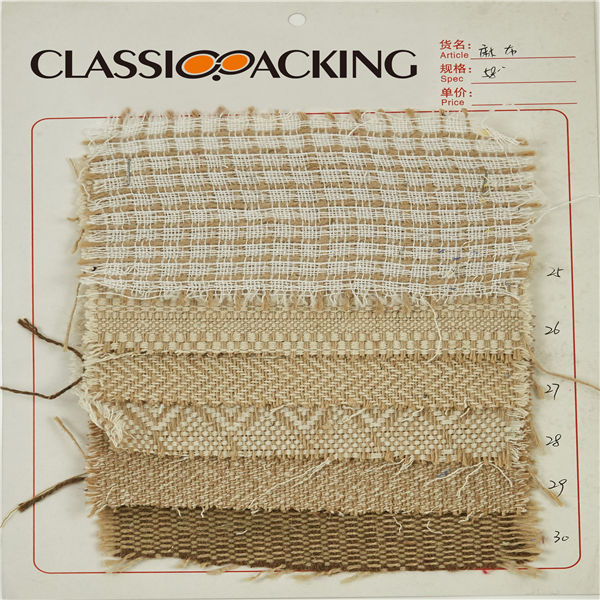 Jute
Jute Jute fibers are composed primarily of the plant materials cellulose and lignin. It falls into the bast fiber category (fiber collected from bast, the phloem of the plant, sometimes called the "skin") along with kenaf, industrial hemp, flax (linen), ramie, etc.
-
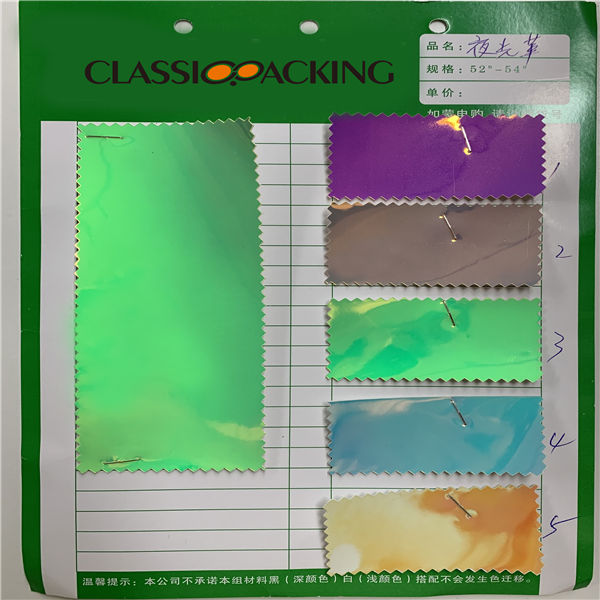 Luminous Fabric
Luminous Fabric Luminous fabric, Fiber Optic fabric, light up fabric. The Luminous Fiber Optic Fabric is a fabric that literally lights up (light emitting fabric / illuminated fabric); It is made of ultra-thin optical fibres, directly woven with synthetic fibers. The fabric is available in several colours.
-
 Multi-color TPU
Multi-color TPU Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of a class of polyurethane plastics with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of linear segmented block copolymers composed of hard and soft segments.
-
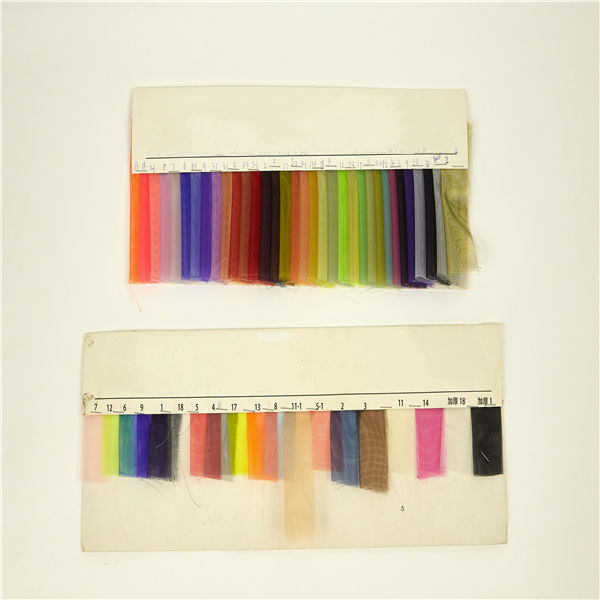 Nylon
Nylon Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers composed of polyamides (repeating units linked by amide links). Nylon is a thermoplastic silky material that can be melt-processed into fibers, films, or shapes.
-
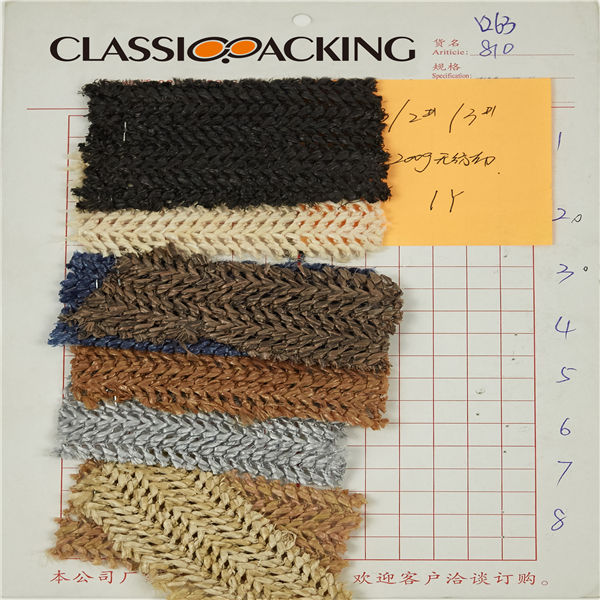 PET
PET PET, which stands for polyethylene terephthalate, is a clear, strong and lightweight plastic belonging to the polyester family. It is typically called "polyester" when used for fibers or fabrics, and "PET" or "PET Resin" when used for bottles, jars, containers and packaging applications.
-
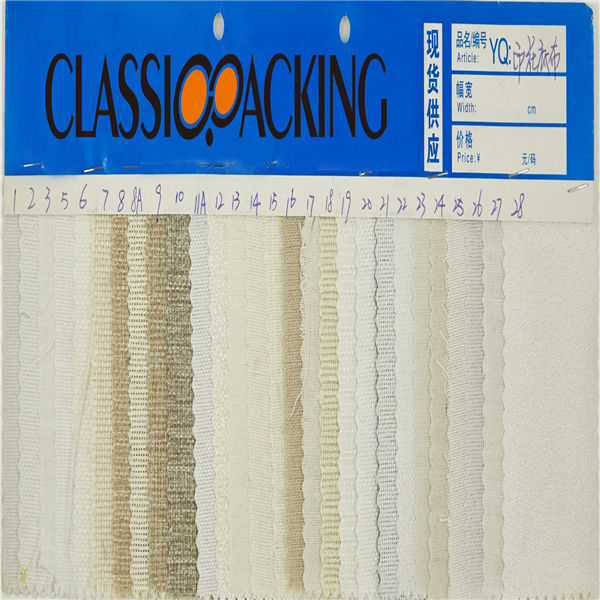 Printed Jute
Printed Jute Jute fibers are composed primarily of the plant materials cellulose and lignin. It falls into the bast fiber category (fiber collected from bast, the phloem of the plant, sometimes called the "skin") along with kenaf, industrial hemp, flax (linen), ramie, etc. The industrial term for jute fiber is raw jute.
-
 Polyamide/Nylon (Artificial Rabbit Fur)
Polyamide/Nylon (Artificial Rabbit Fur) A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
Super soft faux fur fabric! Imitation rabbit!
-
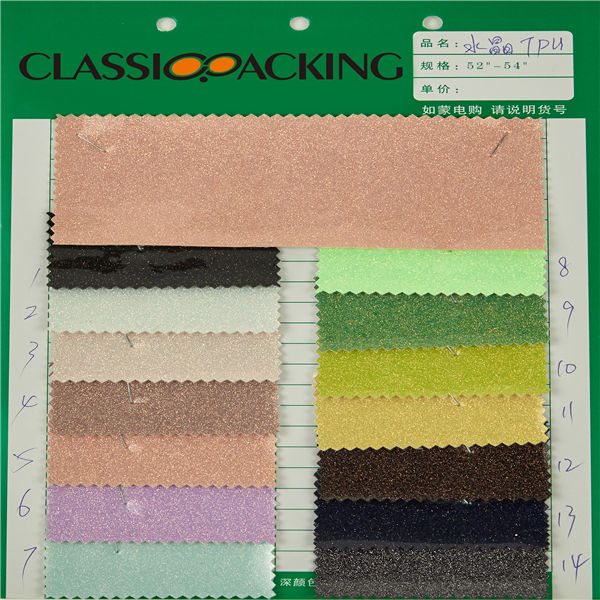 Rubber TPU
Rubber TPU Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of a class of polyurethane plastics with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of linear segmented block copolymers composed of hard and soft segments.
-
 Shining PVC
Shining PVC Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
Except the basic features of normal pvc material, magic color shining PVC fabric, sparkly and funny, easy to attract people's vision.
-
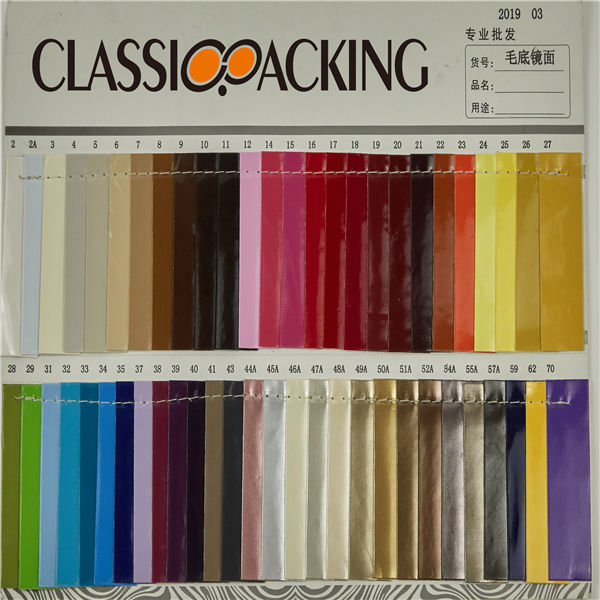 Warnish PU leather
Warnish PU leather PU leather is a split leather that has been laminated with a polyurethane coating to make it look like a top grain leather. Usually, these leathers have a glossy surface and an antique look. PU leather is used for furniture, bags and shoes.
-
 Yangba PU Leather
Yangba PU Leather PU leather is a split leather that has been laminated with a polyurethane coating to make it look like a top grain leather. Usually, these leathers have a glossy surface and an antique look. PU leather is used for furniture, bags and shoes.
-
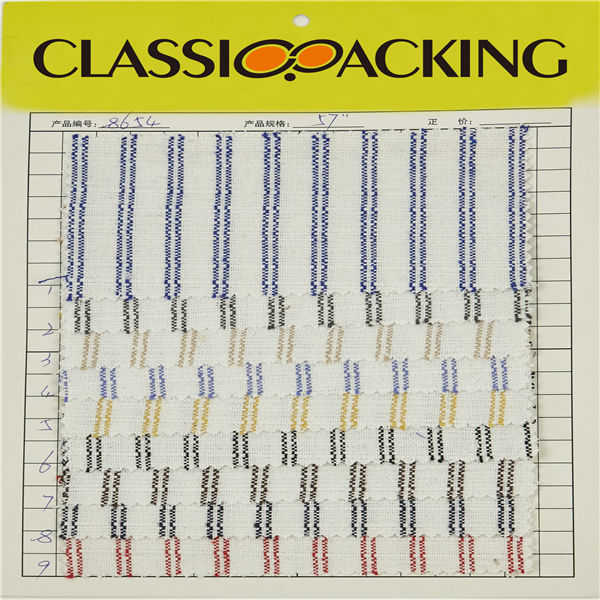 Polyamide (Nylon) 1
Polyamide (Nylon) 1 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
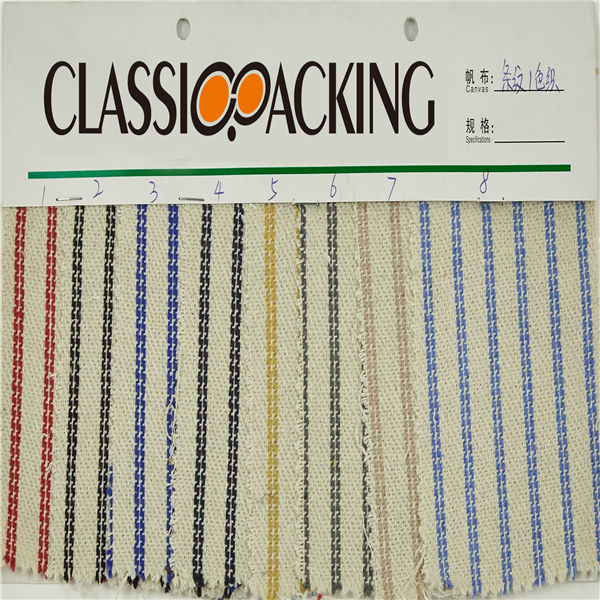 Polyamide (Nylon) 2
Polyamide (Nylon) 2 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 3
Polyamide (Nylon) 3 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
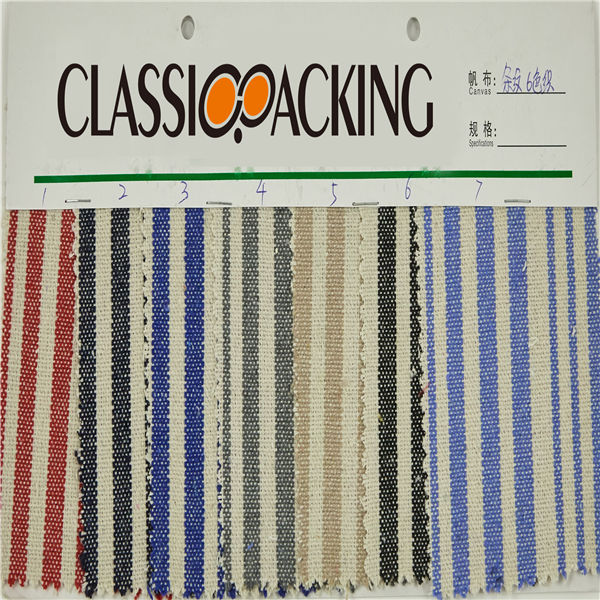 Polyamide (Nylon) 4
Polyamide (Nylon) 4 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 5
Polyamide (Nylon) 5 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
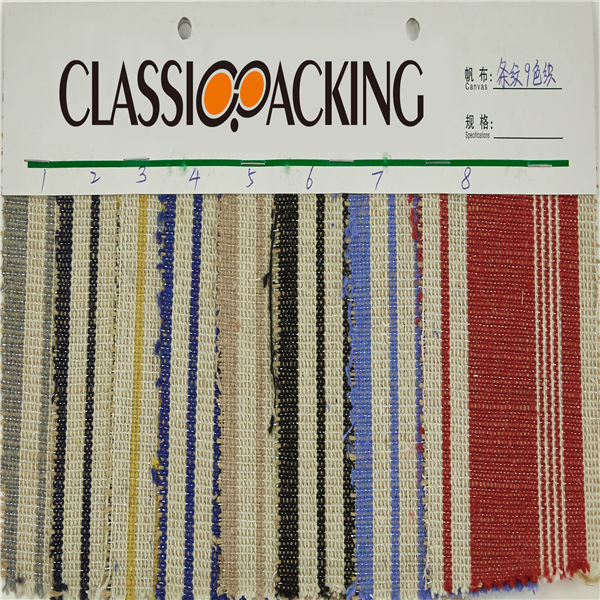 Polyamide (Nylon) 6
Polyamide (Nylon) 6 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
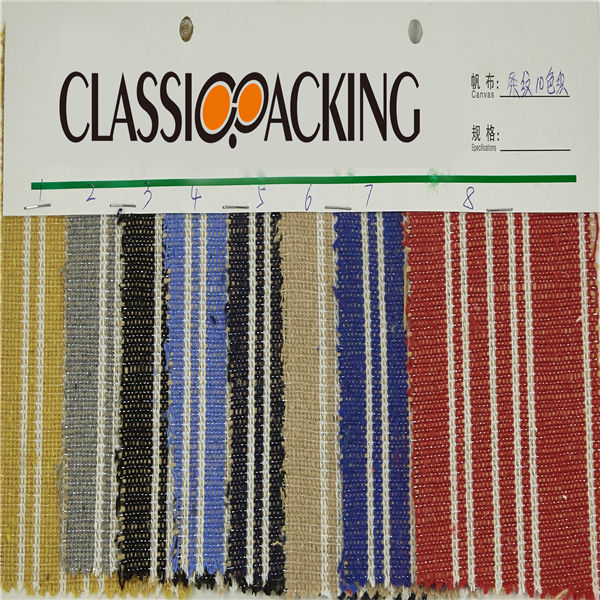 Polyamide (Nylon) 7
Polyamide (Nylon) 7 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 8
Polyamide (Nylon) 8 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 9
Polyamide (Nylon) 9 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 10
Polyamide (Nylon) 10 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 11
Polyamide (Nylon) 11 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 12
Polyamide (Nylon) 12 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
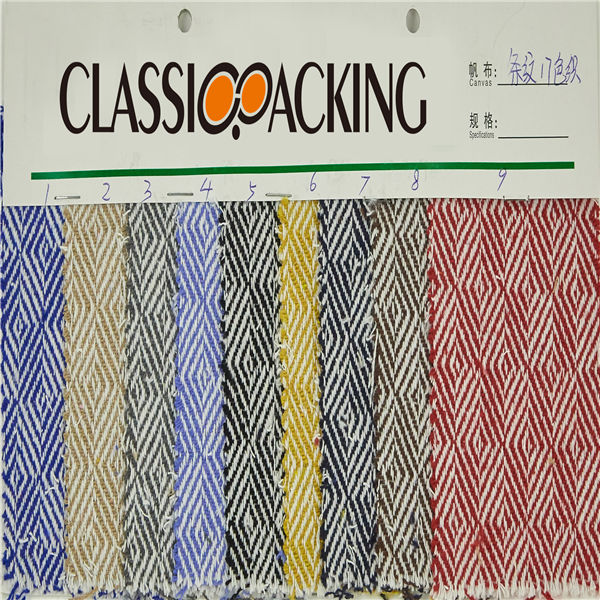 Polyamide (Nylon) 13
Polyamide (Nylon) 13 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
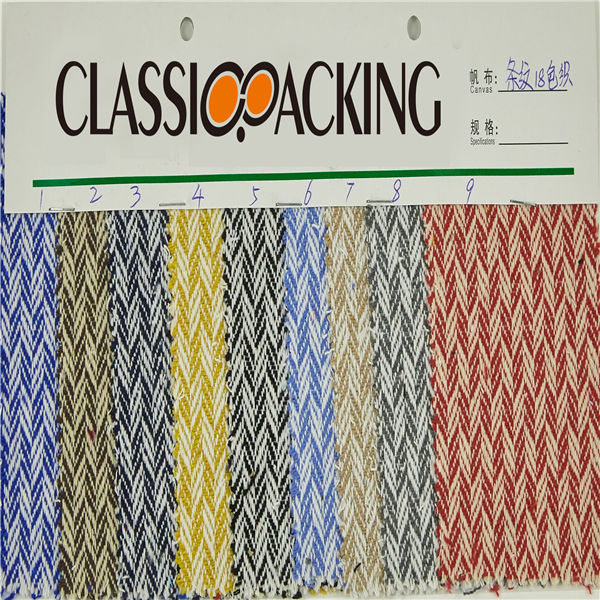 Polyamide (Nylon) 14
Polyamide (Nylon) 14 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 15
Polyamide (Nylon) 15 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 16
Polyamide (Nylon) 16 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 17
Polyamide (Nylon) 17 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 18
Polyamide (Nylon) 18 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 19
Polyamide (Nylon) 19 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 20
Polyamide (Nylon) 20 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
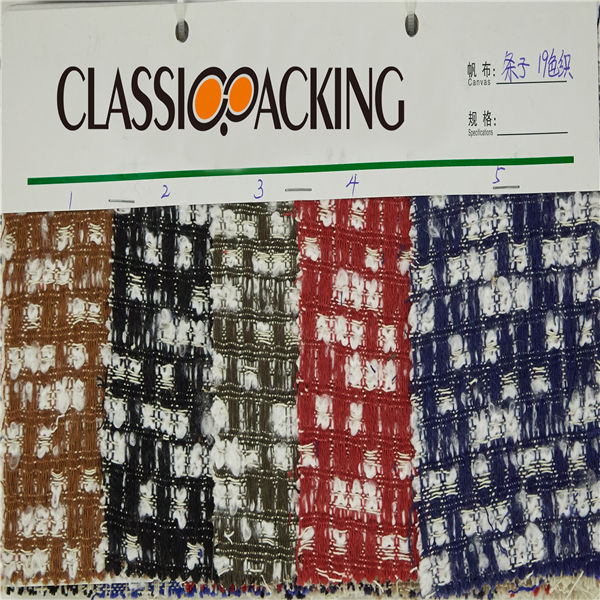 Polyamide (Nylon) 21
Polyamide (Nylon) 21 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 22
Polyamide (Nylon) 22 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 23
Polyamide (Nylon) 23 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
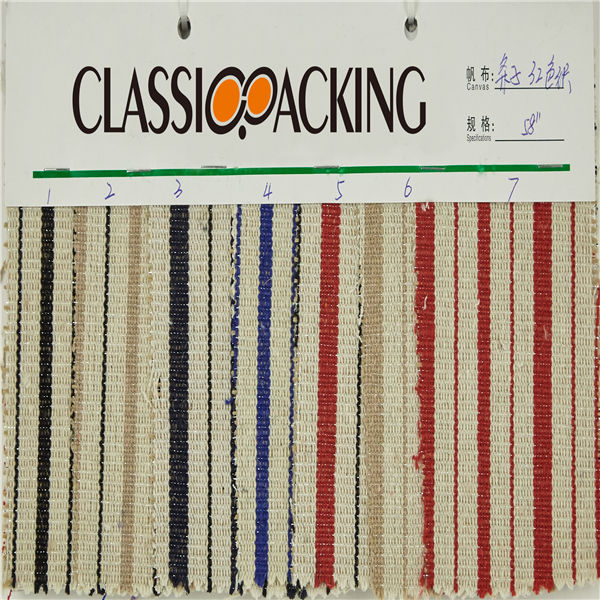 Polyamide (Nylon) 24
Polyamide (Nylon) 24 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 25
Polyamide (Nylon) 25 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
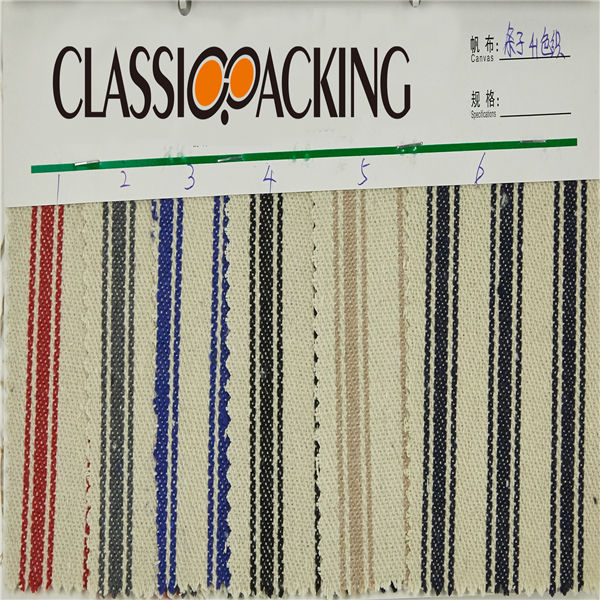 Polyamide (Nylon) 26
Polyamide (Nylon) 26 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
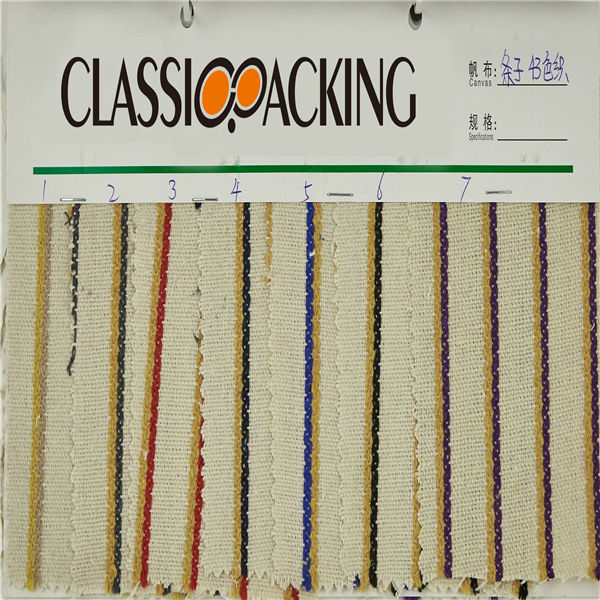 Polyamide (Nylon) 27
Polyamide (Nylon) 27 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 28
Polyamide (Nylon) 28 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Polyamide (Nylon) 29
Polyamide (Nylon) 29 A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk.
-
 Elastic PP Straw 1
Elastic PP Straw 1 Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic “addition polymer” made from the combination of propylene monomers. It is used in a variety of applications to include packaging for consumer products, plastic parts for various industries including the automotive industry, special devices like living hinges, and textiles.
-
 Elastic PP Straw 2
Elastic PP Straw 2 Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic “addition polymer” made from the combination of propylene monomers. It is used in a variety of applications to include packaging for consumer products, plastic parts for various industries including the automotive industry, special devices like living hinges, and textiles.
-
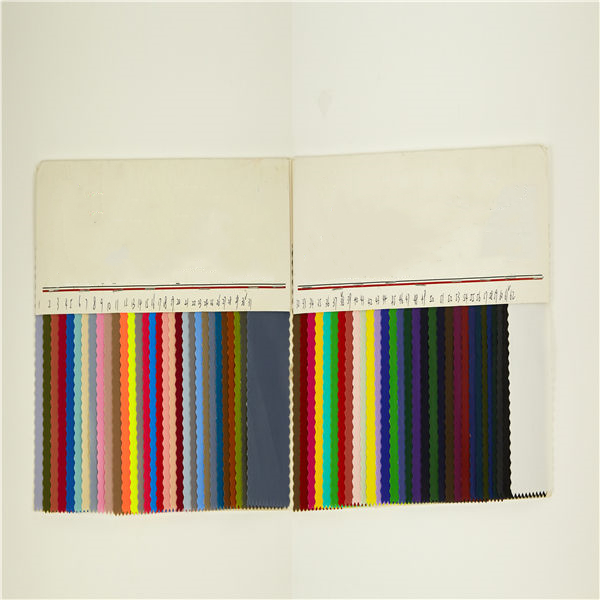 Memory Fabric 1
Memory Fabric 1 Memory fabrics so produced are novel fabrics which respond to the temperature stimulation. The concept of shape memory fabric is new and these fabrics were prepared by applying waterborne shape memory polymers in Polyurethane series (SMP) onto fabrics through specific finishing processes.
-
 Memory Fabric 2
Memory Fabric 2 Memory fabrics so produced are novel fabrics which respond to the temperature stimulation. The concept of shape memory fabric is new and these fabrics were prepared by applying waterborne shape memory polymers in Polyurethane series (SMP) onto fabrics through specific finishing processes.
-
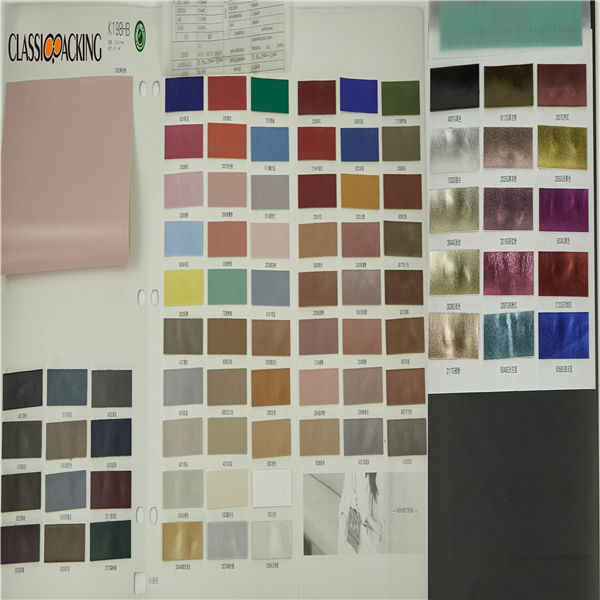
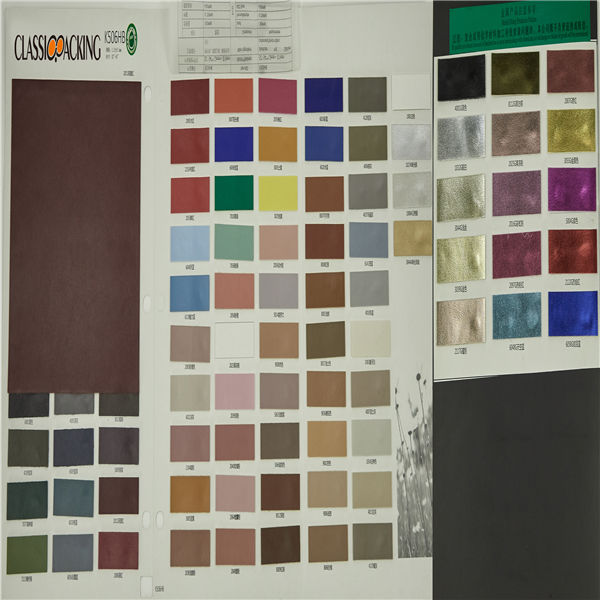
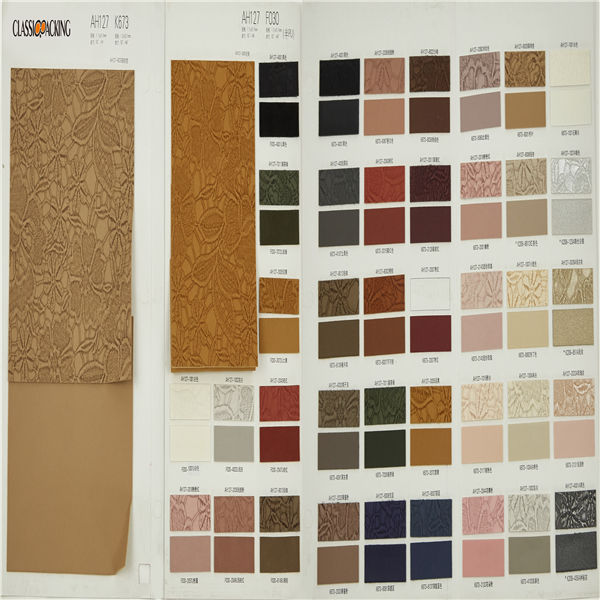 Semi-Pu 1
Semi-Pu 1 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 2
Semi-Pu 2 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
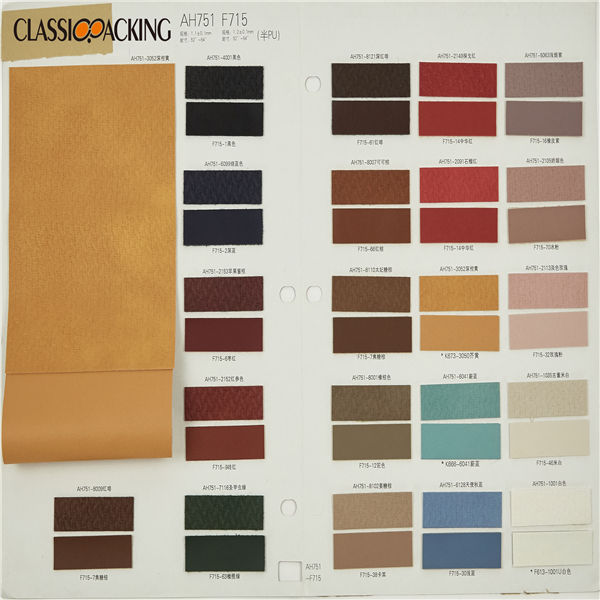 Semi-Pu 3
Semi-Pu 3 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
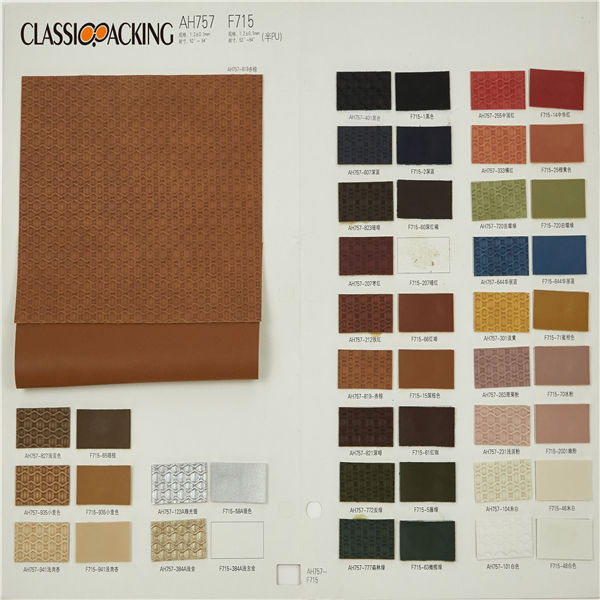 Semi-Pu 4
Semi-Pu 4 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 5
Semi-Pu 5 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
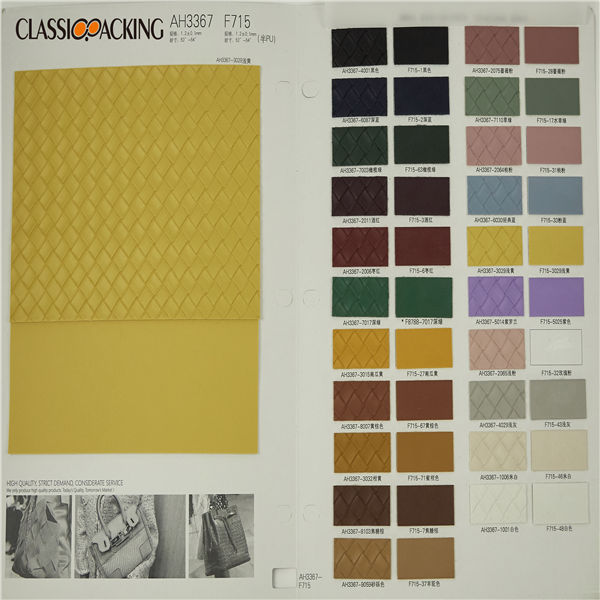 Semi-Pu 6
Semi-Pu 6 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 7
Semi-Pu 7 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 8
Semi-Pu 8 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 9
Semi-Pu 9 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 10
Semi-Pu 10 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 11
Semi-Pu 11 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 12
Semi-Pu 12 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
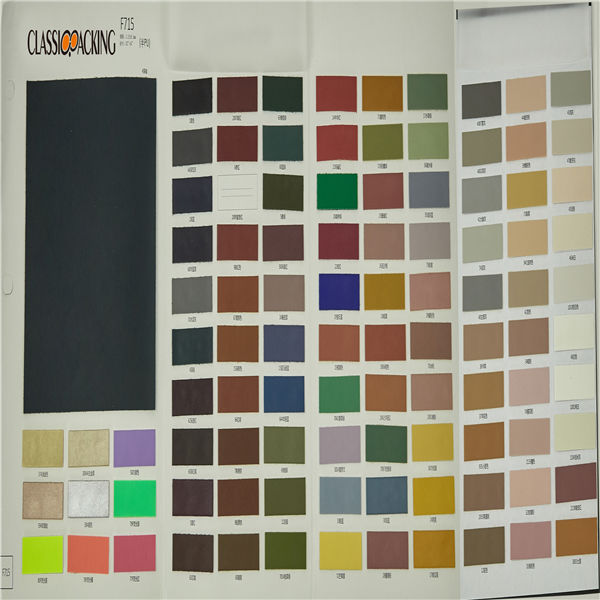 Semi-Pu 13
Semi-Pu 13 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 14
Semi-Pu 14 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 15
Semi-Pu 15 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 16
Semi-Pu 16 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
 Semi-Pu 17
Semi-Pu 17 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
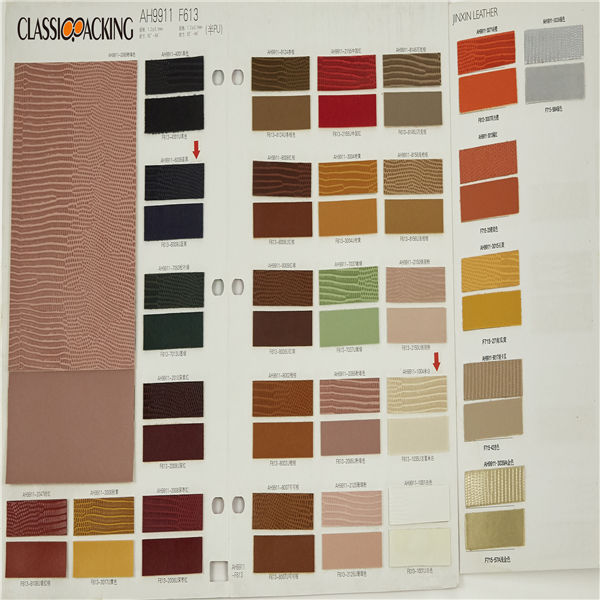 Semi-PU 18
Semi-PU 18 Semi-PU leather is a type of faux leather fabric features between PVC leather and PU leather. Manufactured with particular ratio of synthetic substances, these semi-PU leather are compromises between PVC and PU leather, so as to be comparable softer than PVC. Because of the ingredient of semi-PU leather fabrics, they are comparably cheapest, thus, to be welcomed by various cosmetic bag manufacturers.
-
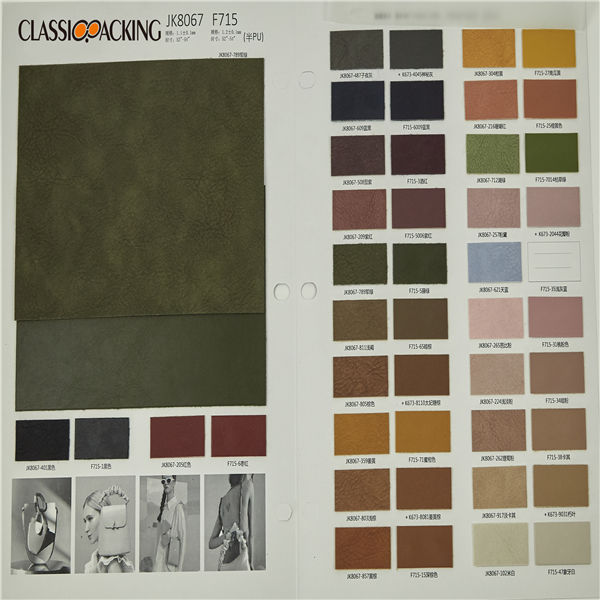
 PU 1
PU 1 PU leather is a split leather that has been laminated with a polyurethane coating to make it look like a top grain leather. Usually, these leathers have a glossy surface and an antique look. PU leather is used for furniture, bags and shoes.
-
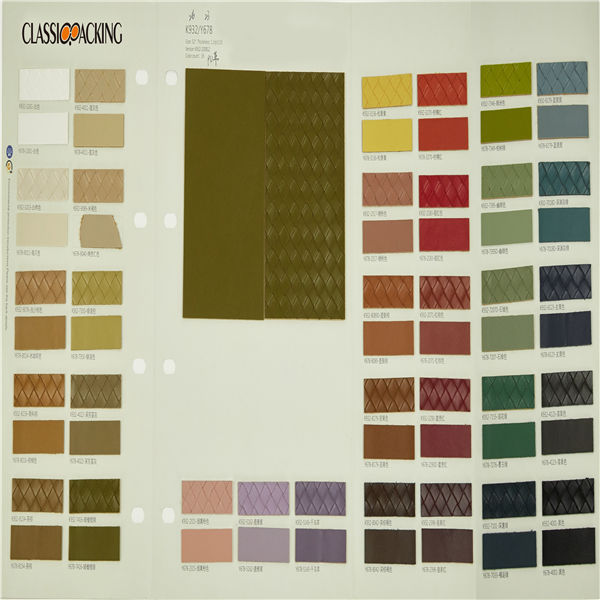 PU 2
PU 2 PU leather is a split leather that has been laminated with a polyurethane coating to make it look like a top grain leather. Usually, these leathers have a glossy surface and an antique look. PU leather is used for furniture, bags and shoes.
-
 PU 3
PU 3 PU leather is a split leather that has been laminated with a polyurethane coating to make it look like a top grain leather. Usually, these leathers have a glossy surface and an antique look. PU leather is used for furniture, bags and shoes.
-
 PU 4
PU 4 PU leather is a split leather that has been laminated with a polyurethane coating to make it look like a top grain leather. Usually, these leathers have a glossy surface and an antique look. PU leather is used for furniture, bags and shoes.
-
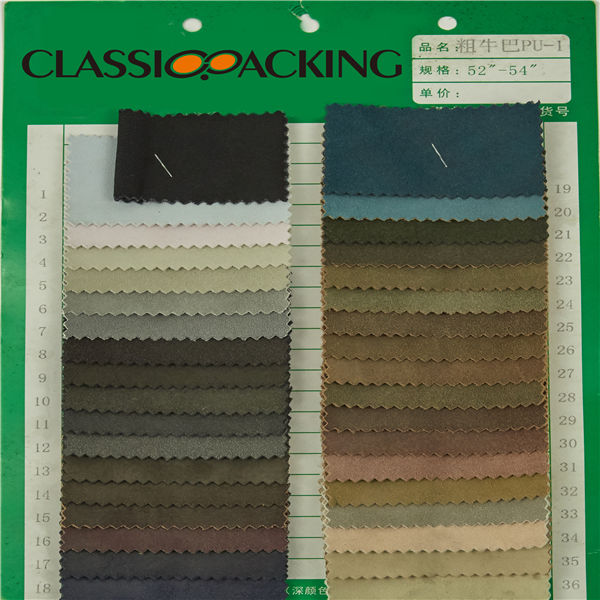 PU 5
PU 5 PU leather is a split leather that has been laminated with a polyurethane coating to make it look like a top grain leather. Usually, these leathers have a glossy surface and an antique look. PU leather is used for furniture, bags and shoes.
-
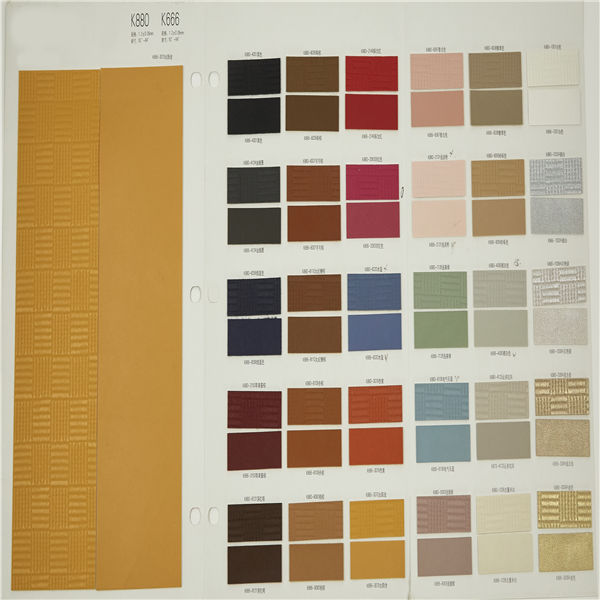
 PVC 1
PVC 1 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
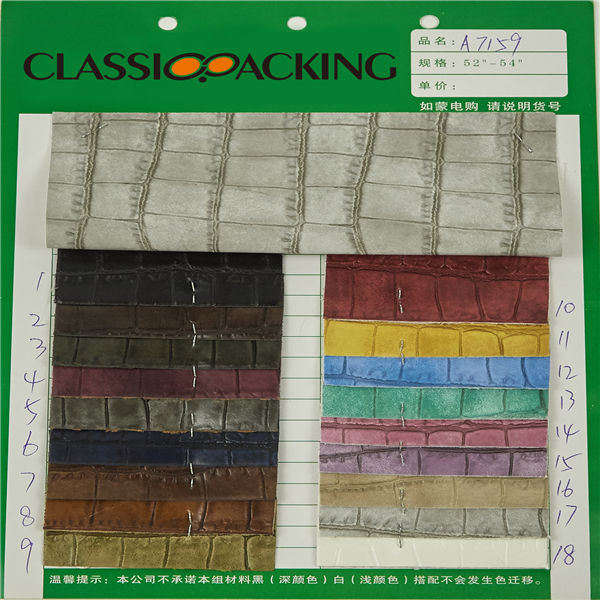 PVC 2
PVC 2 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
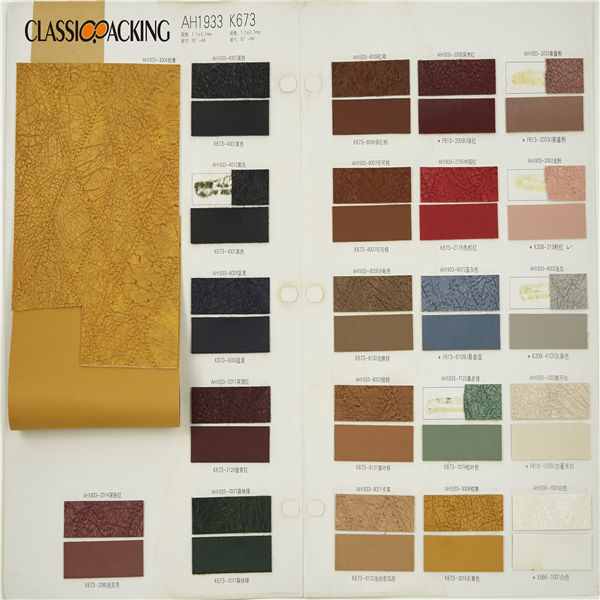 PVC 3
PVC 3 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
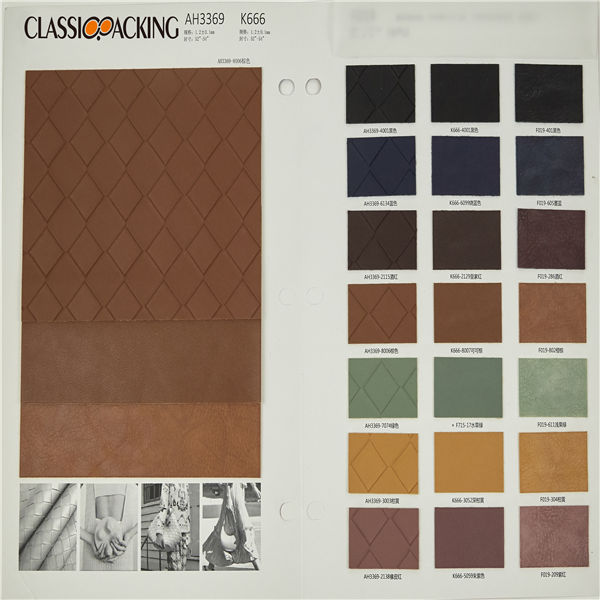 PVC 4
PVC 4 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 5
PVC 5 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
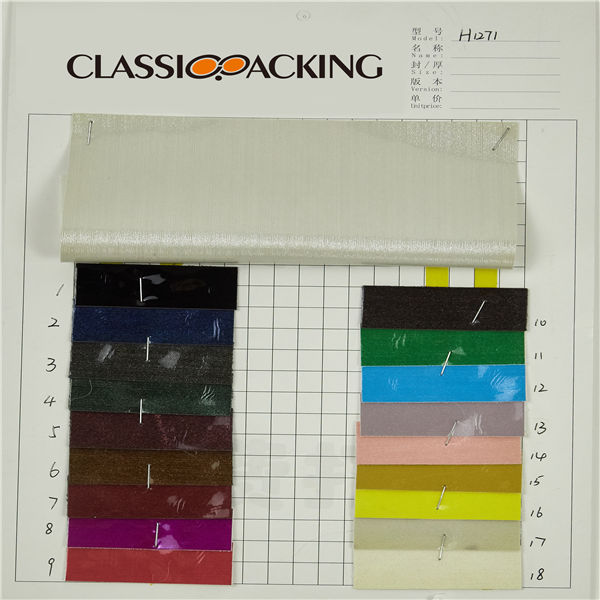
 PVC 6
PVC 6 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 7
PVC 7 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
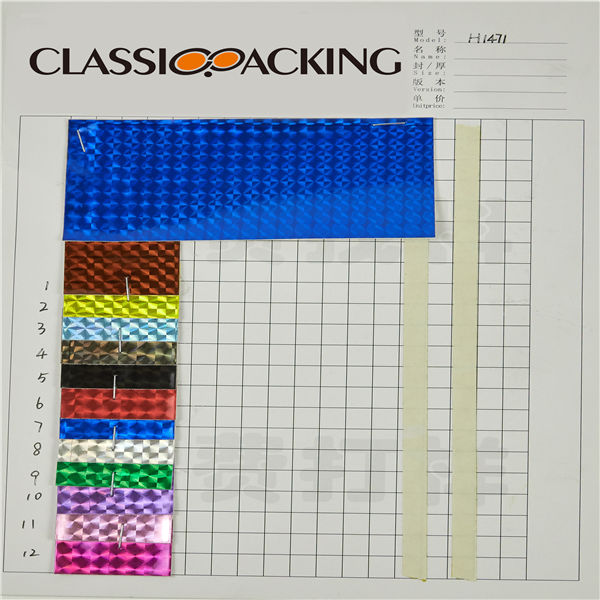 PVC 8
PVC 8 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
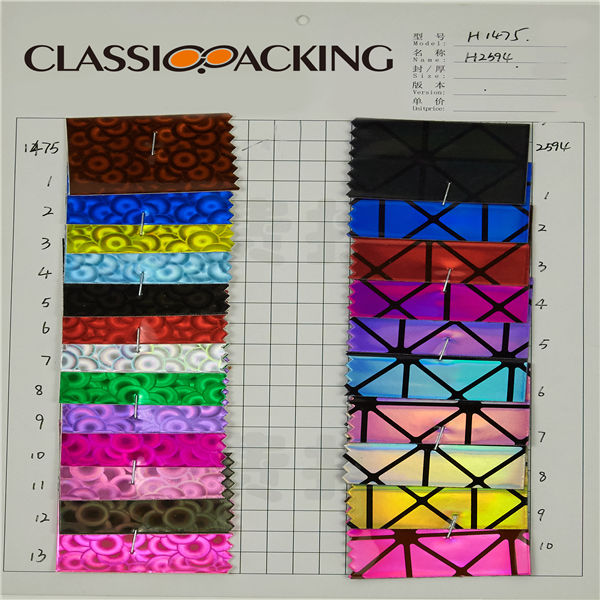 PVC 9
PVC 9 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
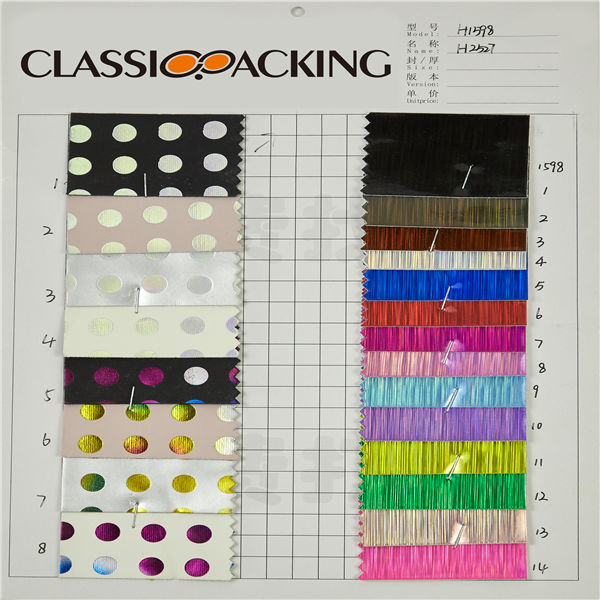 PVC 10
PVC 10 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
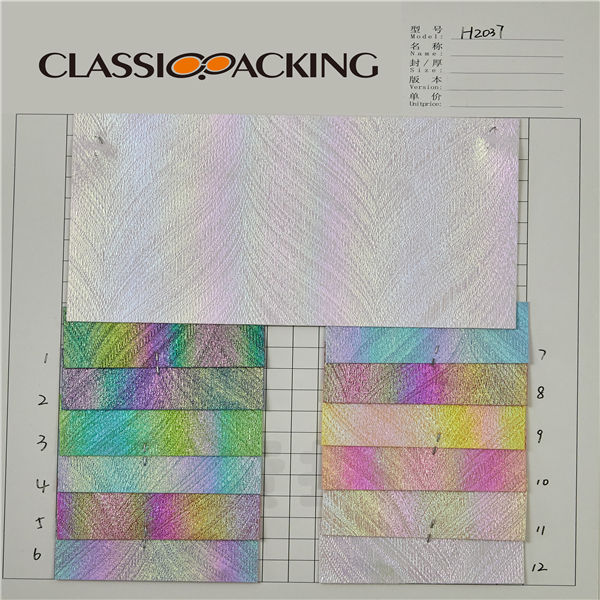 PVC 11
PVC 11 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
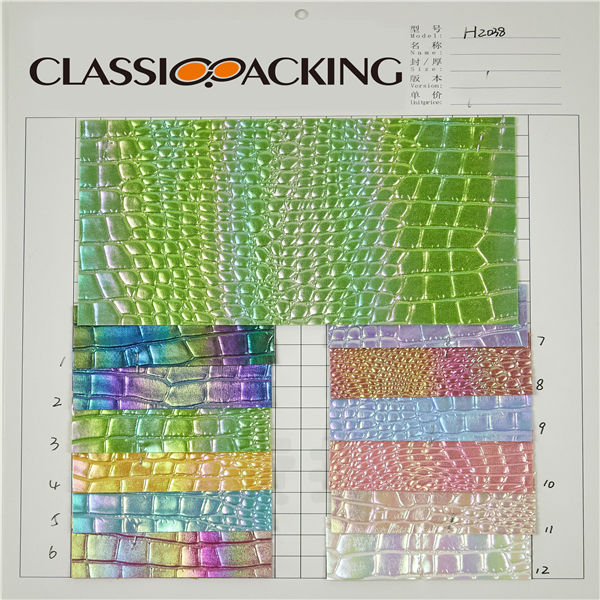 PVC 12
PVC 12 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
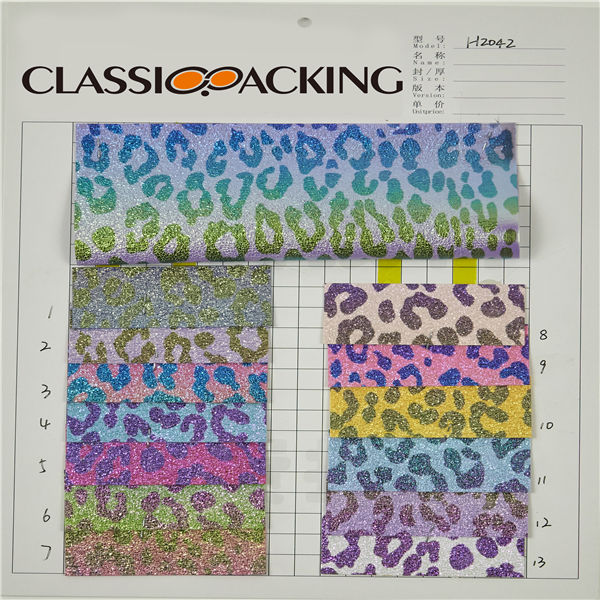 PVC 13
PVC 13 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
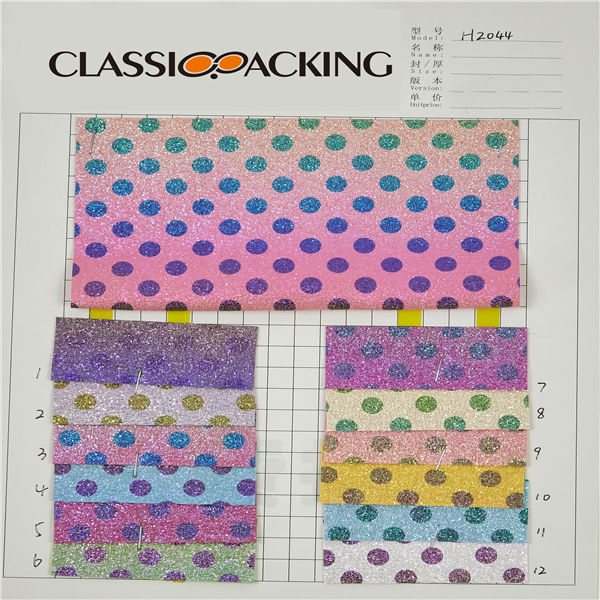 PVC 14
PVC 14 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
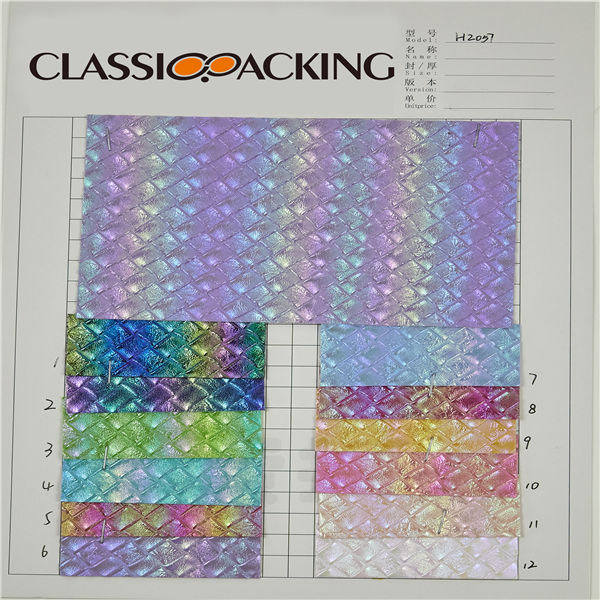 PVC 15
PVC 15 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 16
PVC 16 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 17
PVC 17 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
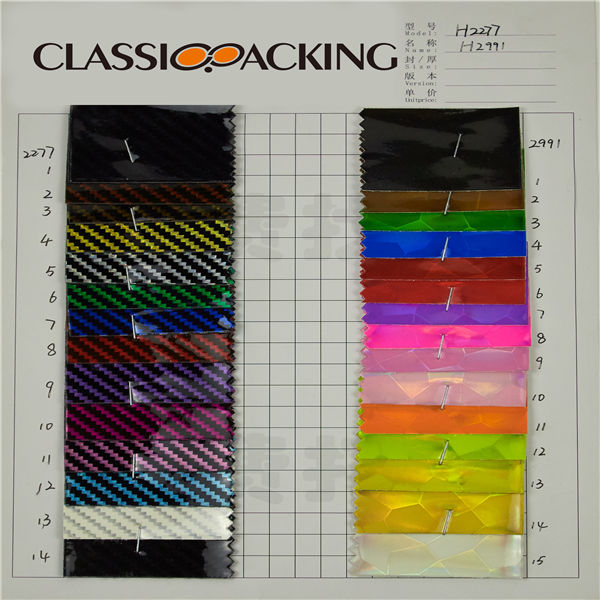 PVC 18
PVC 18 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 19
PVC 19 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
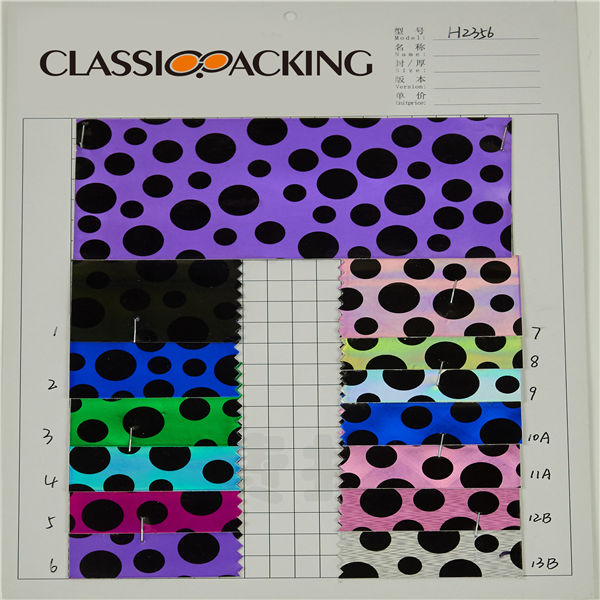 PVC 20
PVC 20 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 21
PVC 21 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
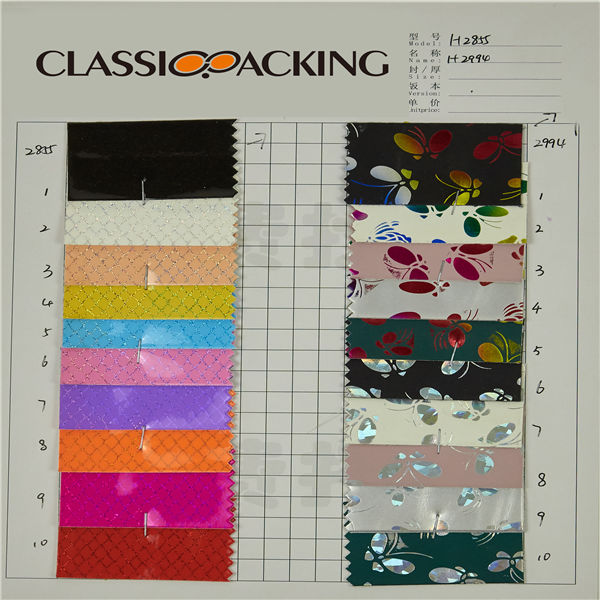 PVC 22
PVC 22 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
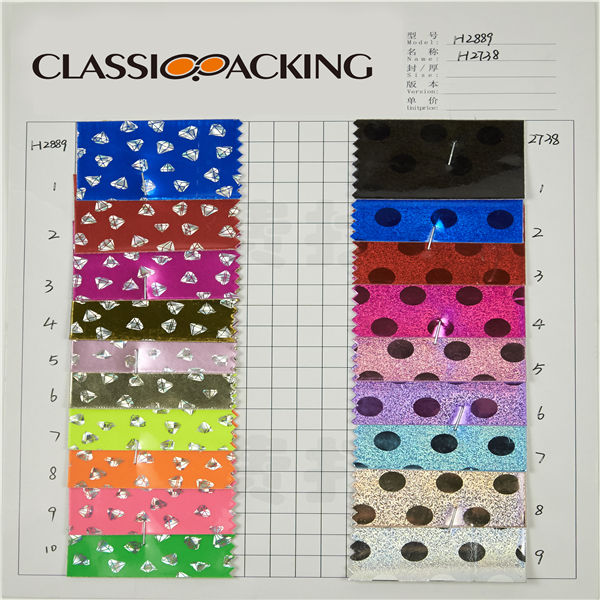 PVC 23
PVC 23 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 24
PVC 24 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
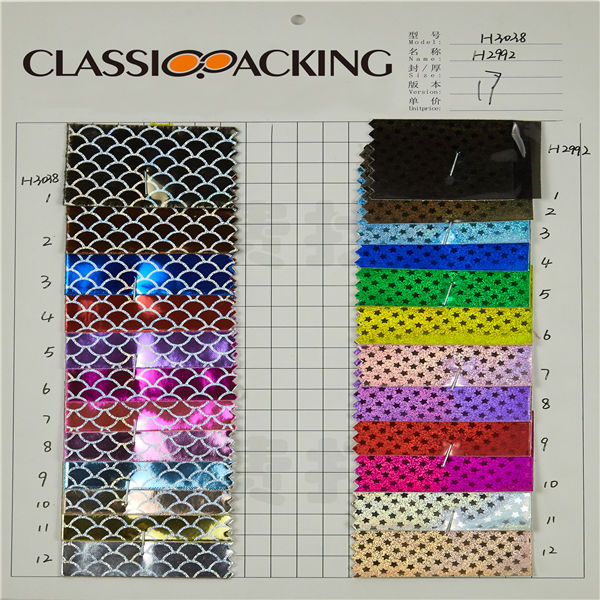 PVC 25
PVC 25 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 26
PVC 26 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 27
PVC 27 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 28
PVC 28 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 29
PVC 29 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 30
PVC 30 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
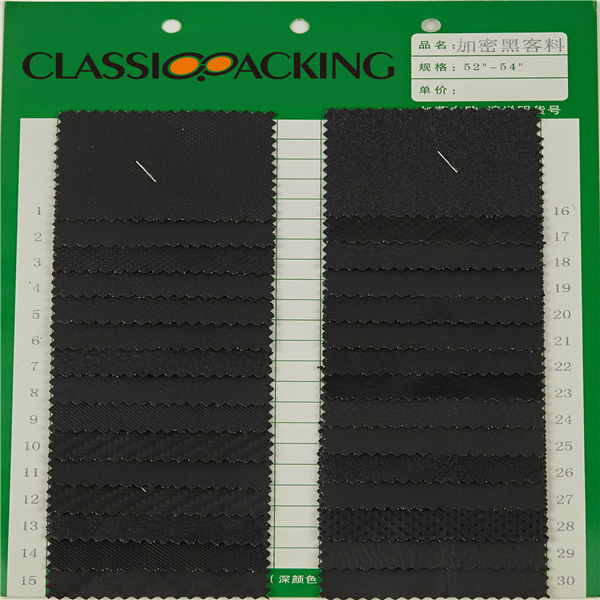 PVC 31
PVC 31 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
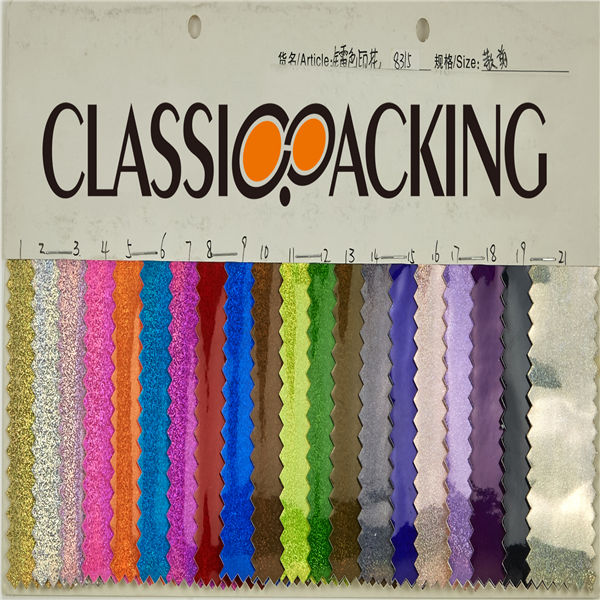 PVC 32
PVC 32 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 33
PVC 33 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 34
PVC 34 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
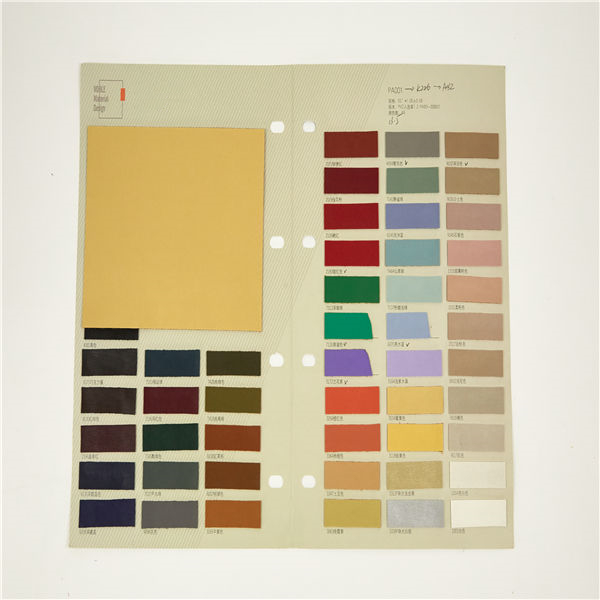 PVC 35
PVC 35 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
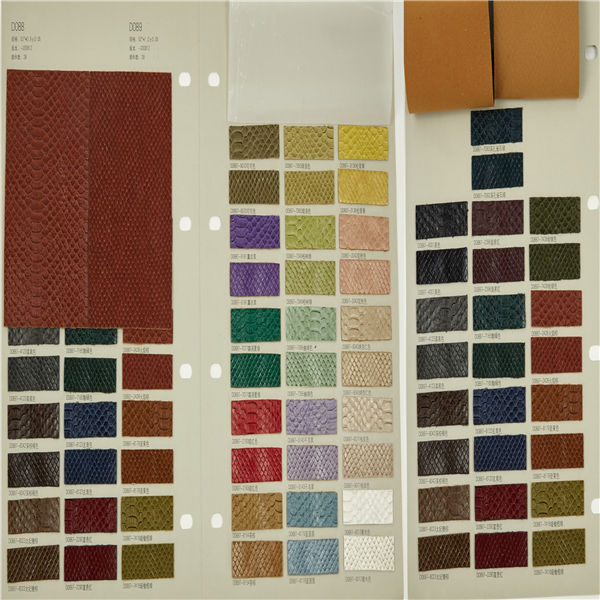 PVC 36
PVC 36 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 PVC 37
PVC 37 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
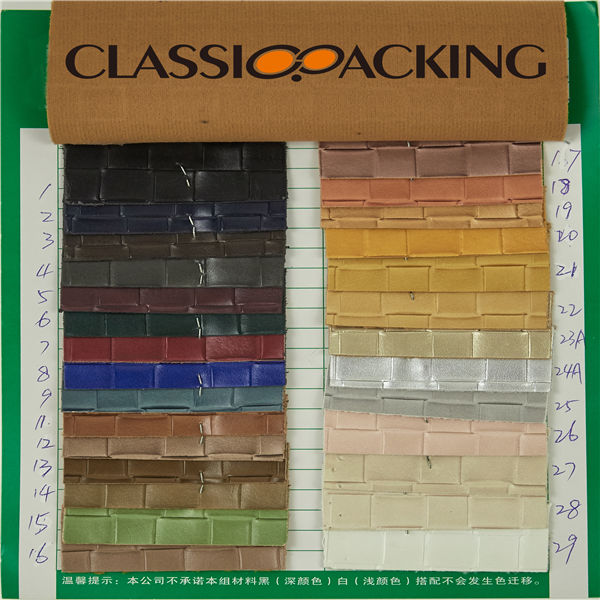
 PVC 38
PVC 38 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
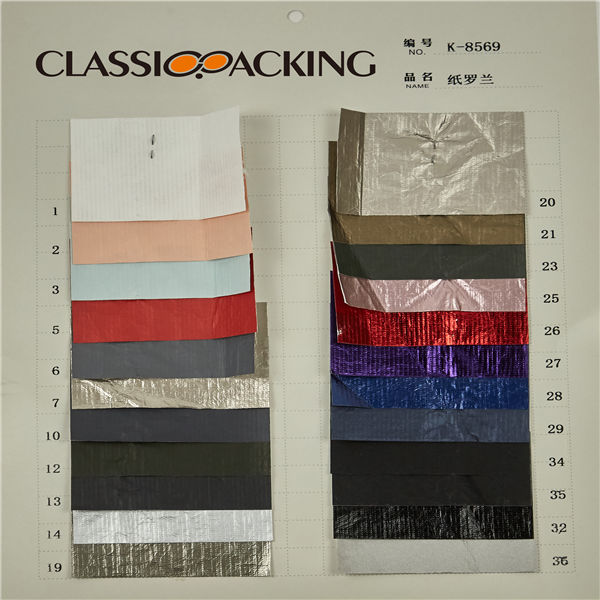
 PVC 39
PVC 39 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
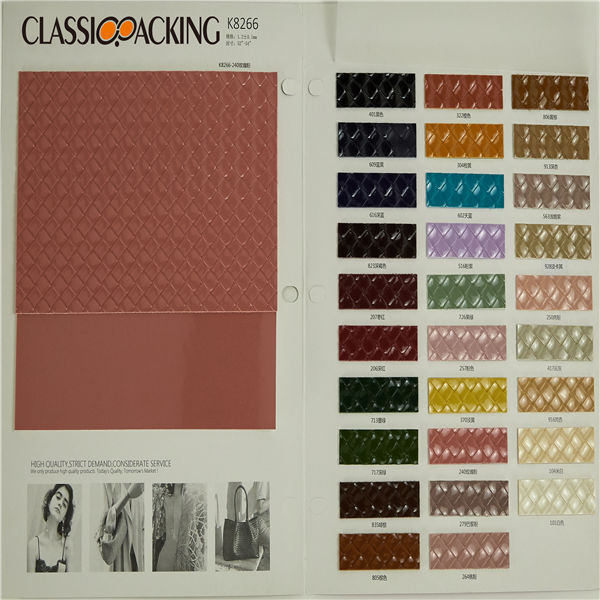 PVC 40
PVC 40 Polyvinyl chloride (colloquial: polyvinyl, vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible.
-
 Cotton 1
Cotton 1 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 2
Cotton 2 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
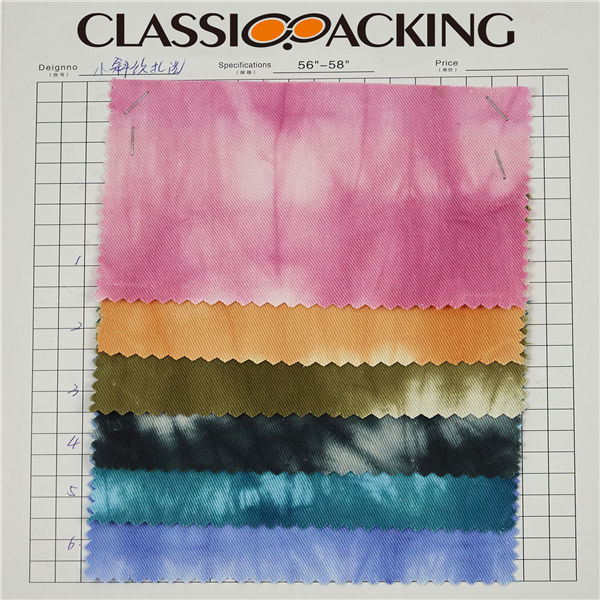 Cotton 3
Cotton 3 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 4
Cotton 4 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
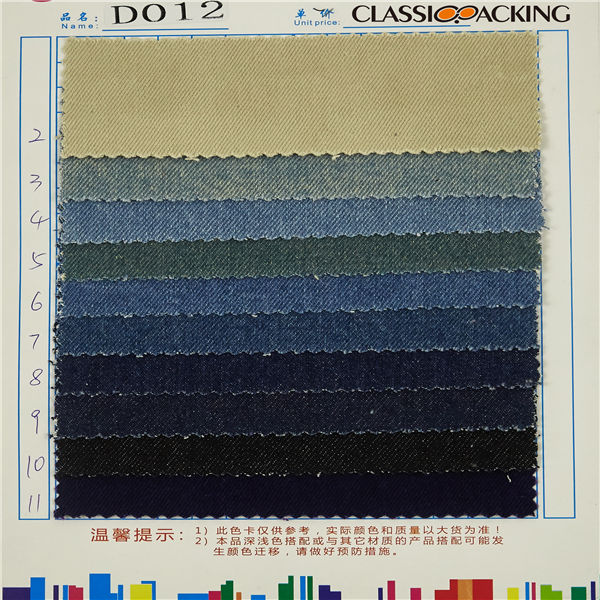 Cotton 5
Cotton 5 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 6
Cotton 6 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
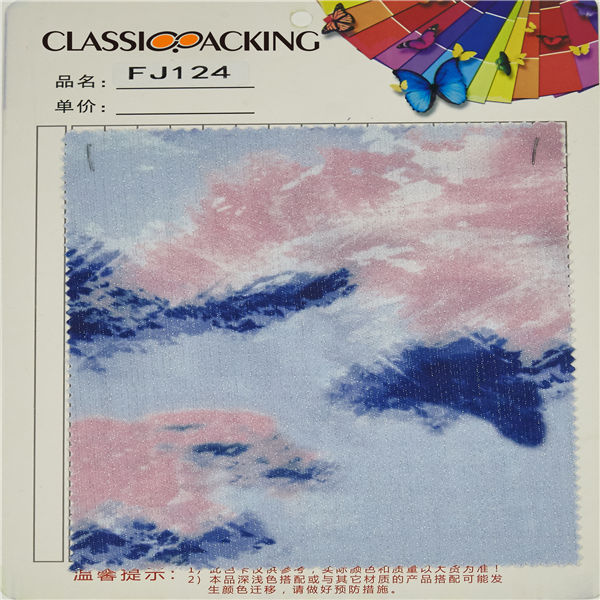 Cotton 7
Cotton 7 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 8
Cotton 8 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 9
Cotton 9 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 10
Cotton 10 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 11
Cotton 11 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
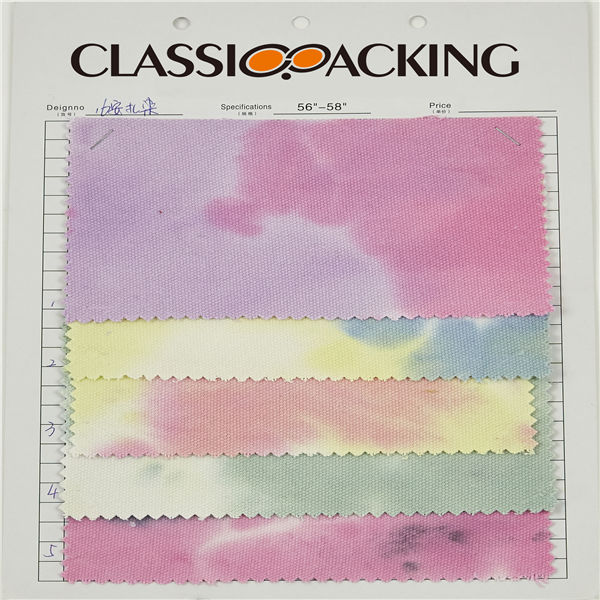 Cotton 12
Cotton 12 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 13
Cotton 13 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Cotton 14
Cotton 14 Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable textile.
-
 Linen-cotton 2
Linen-cotton 2 Linen-cotton is durable, breathable, soft fabric derived from natural fibers. Both cotton and linen are eco-friendly fabrics because they are made from natural fibers.
-
 Linen-cotton 1
Linen-cotton 1 Linen-cotton is durable, breathable, soft fabric derived from natural fibers. Both cotton and linen are eco-friendly fabrics because they are made from natural fibers.
-
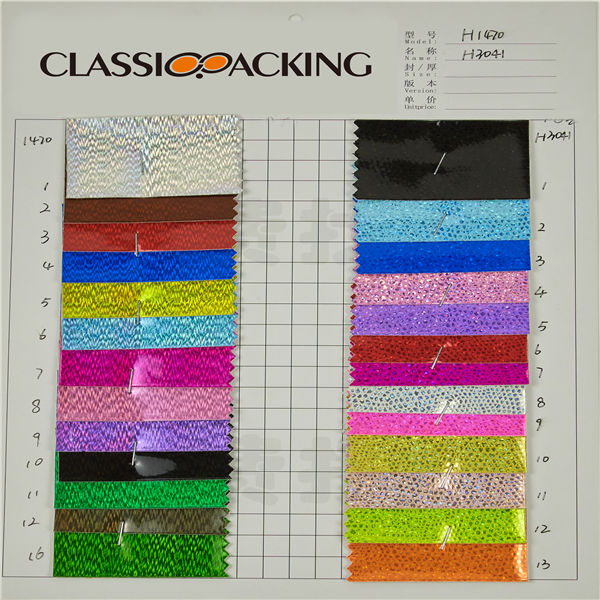
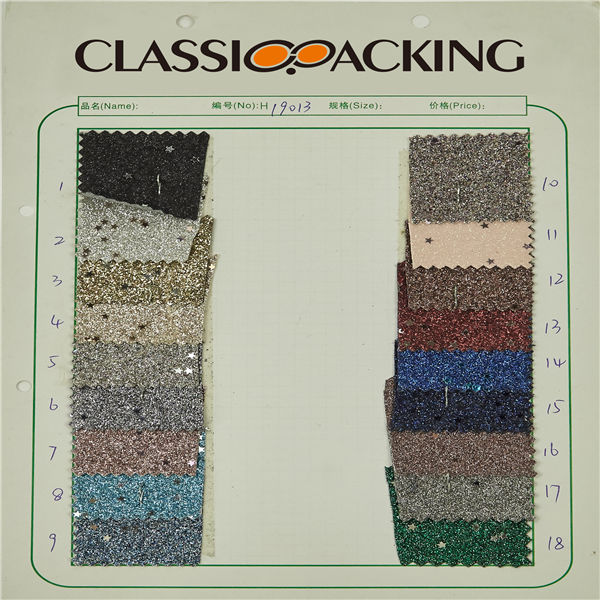
 Glitter 1
Glitter 1 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 2
Glitter 2 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 3
Glitter 3 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 4
Glitter 4 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 5
Glitter 5 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 6
Glitter 6 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 7
Glitter 7 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 8
Glitter 8 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 9
Glitter 9 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 10
Glitter 10 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 11
Glitter 11 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 12
Glitter 12 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Glitter 13
Glitter 13 Glitter fabric is springing up all over the place, creating a sparkling sensation wherever it goes. In turn, the fabric itself has been seen by more and more members of the public and business owners. People who may have never seen such a fabric before, now have to have it for their homes, their business and events.
-
 Linen 1
Linen 1 Linen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant. Linen is very strong and absorbent and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in cosmetic bags.
-
 Linen 2
Linen 2 Linen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant. Linen is very strong and absorbent and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in cosmetic bags.
-
 Linen 3
Linen 3 Linen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant. Linen is very strong and absorbent and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in cosmetic bags.
-
 TPU 2
TPU 2 Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of a class of polyurethane plastics with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of linear segmented block copolymers composed of hard and soft segments.
-
 TPU 1
TPU 1 Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of a class of polyurethane plastics with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of linear segmented block copolymers composed of hard and soft segments.
-
 Polyester 1
Polyester 1 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 2
Polyester 2 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
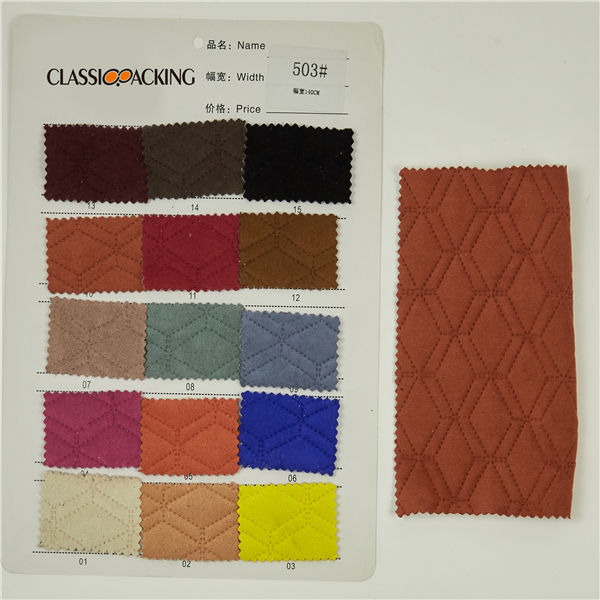 Polyester 3
Polyester 3 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
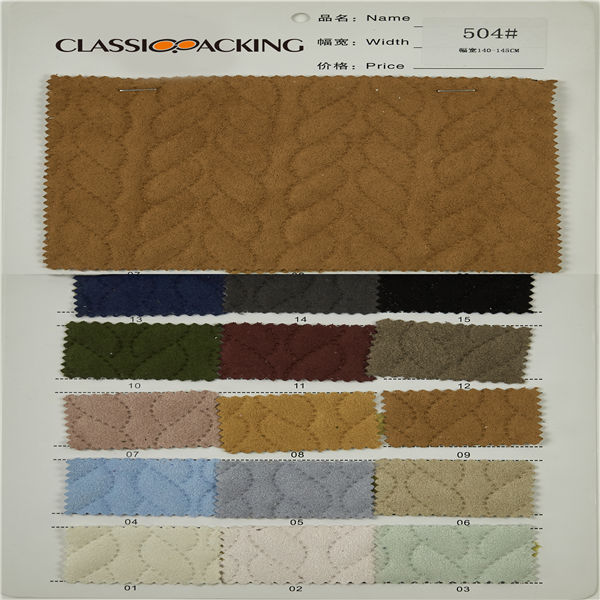 Polyester 4
Polyester 4 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 5
Polyester 5 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 6
Polyester 6 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 7
Polyester 7 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 8
Polyester 8 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 9
Polyester 9 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
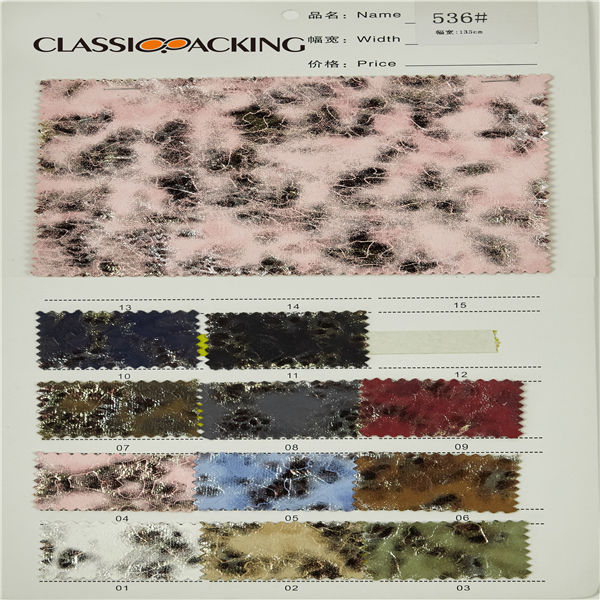 Polyester 10
Polyester 10 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
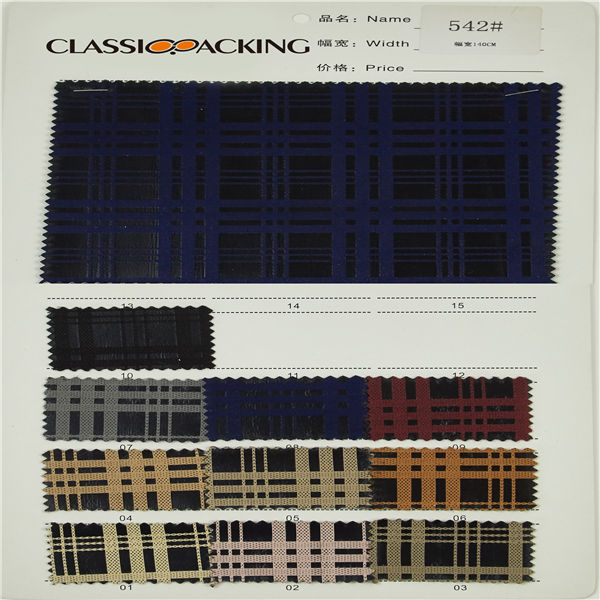 Polyester 11
Polyester 11 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
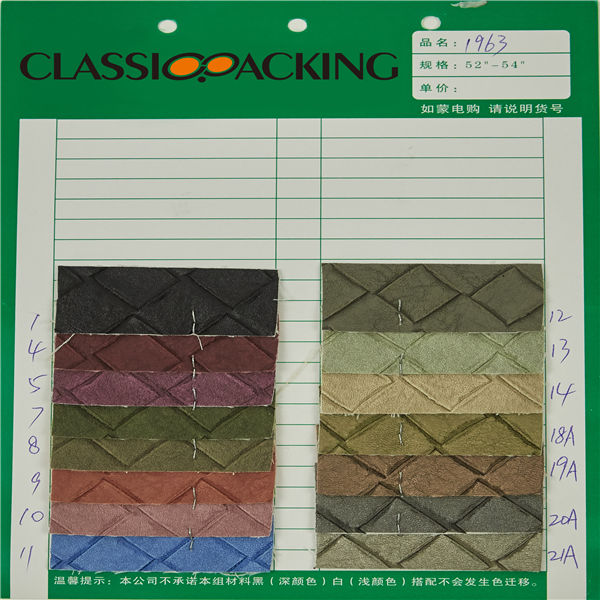 Polyester 12
Polyester 12 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 13
Polyester 13 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
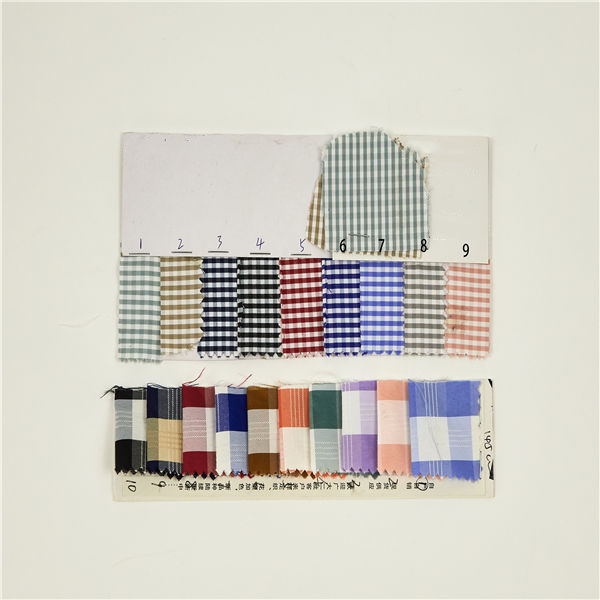 Polyester 14
Polyester 14 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 15
Polyester 15 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
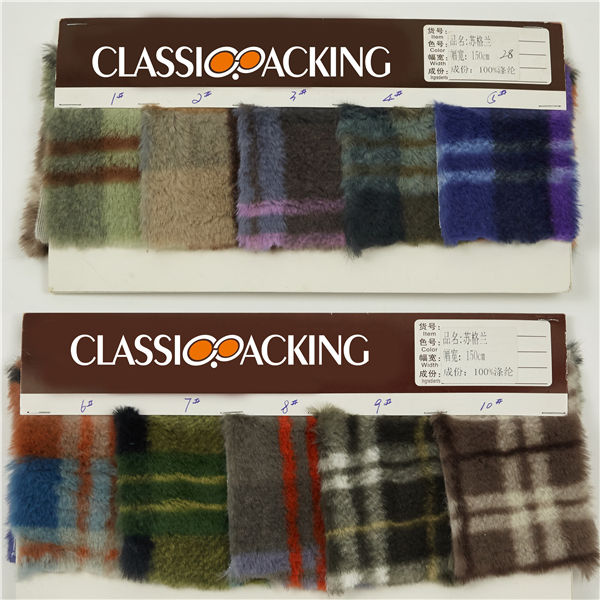 Polyester 16
Polyester 16 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
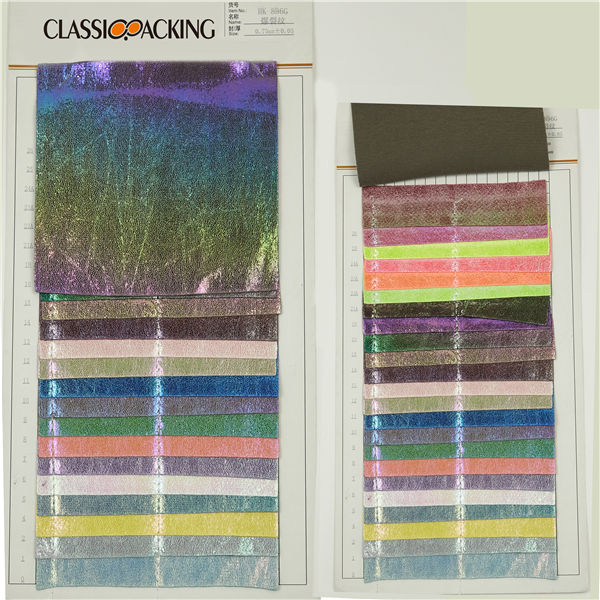 Polyester 17
Polyester 17 Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.
-
 Polyester 18
Polyester 18 (Two Sided Herringbone) Polyester is a generalised term for any fabric or textile, which is made using polyester yarns or fibres. It is a shortened name for a synthetic, man-made polymer, which, as a specific material, is most commonly referred to as a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is made by mixing ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. That all sounds extremely scientific, but basically, polyester is a kind of plastic.





